Blenheim Estate
Oxfordshire, UK
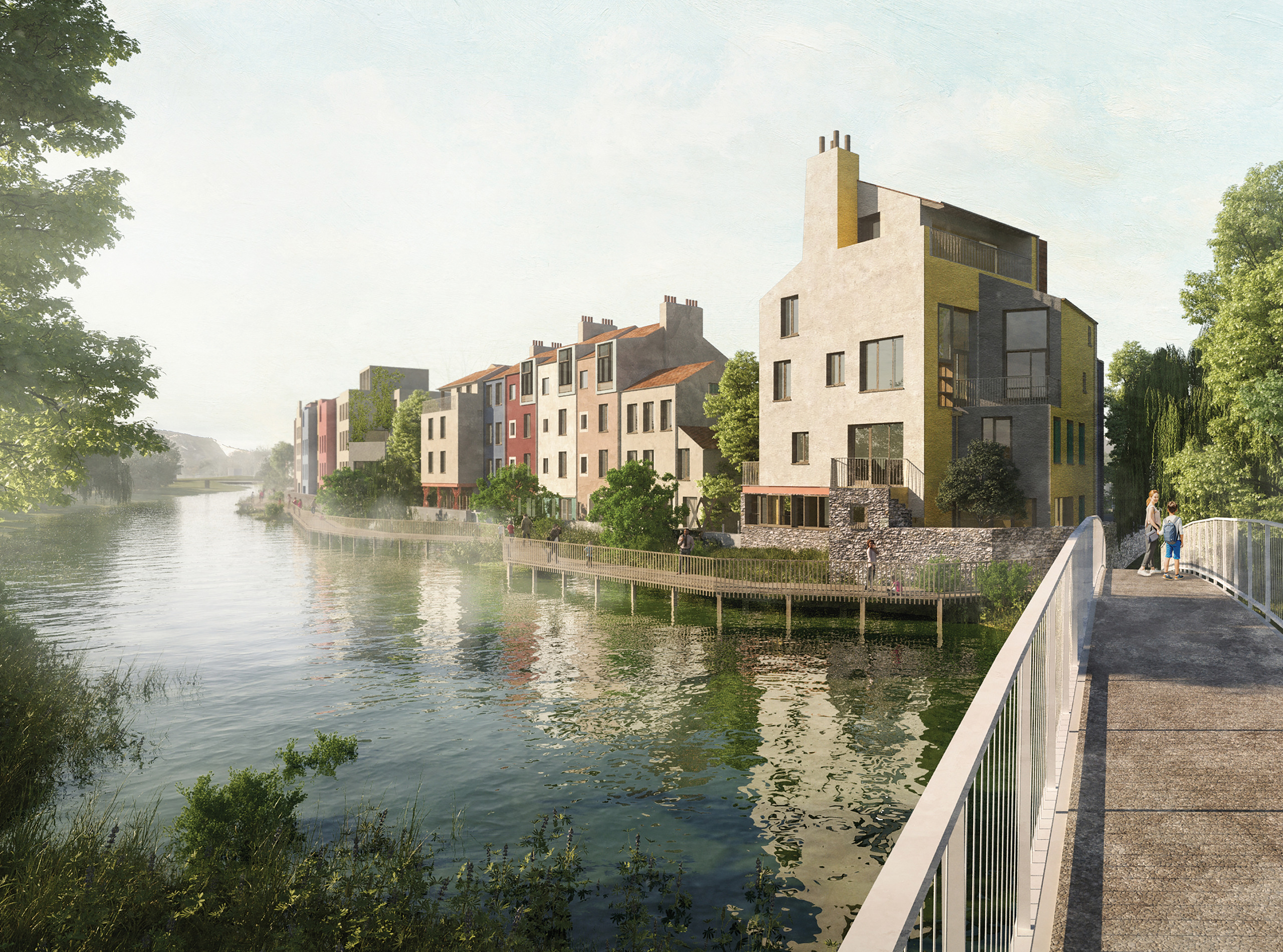
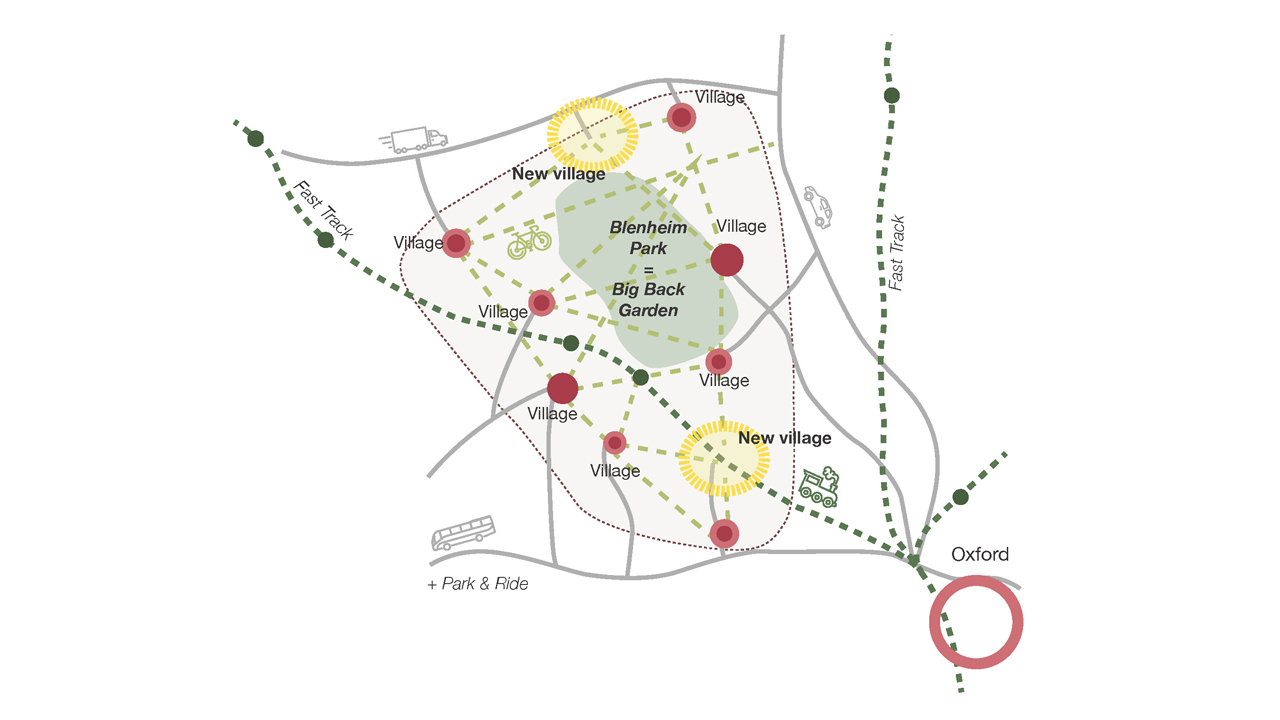
Expedition developed the infrastructure strategies for sustainable village growth across the Blenheim Estate, addressing critical challenges facing rural communities in the 21st century. Incorporating VeloCity principles, we created innovative approaches that enable the villages and communities surrounding Britain's greatest palace to thrive within the current climate crisis.
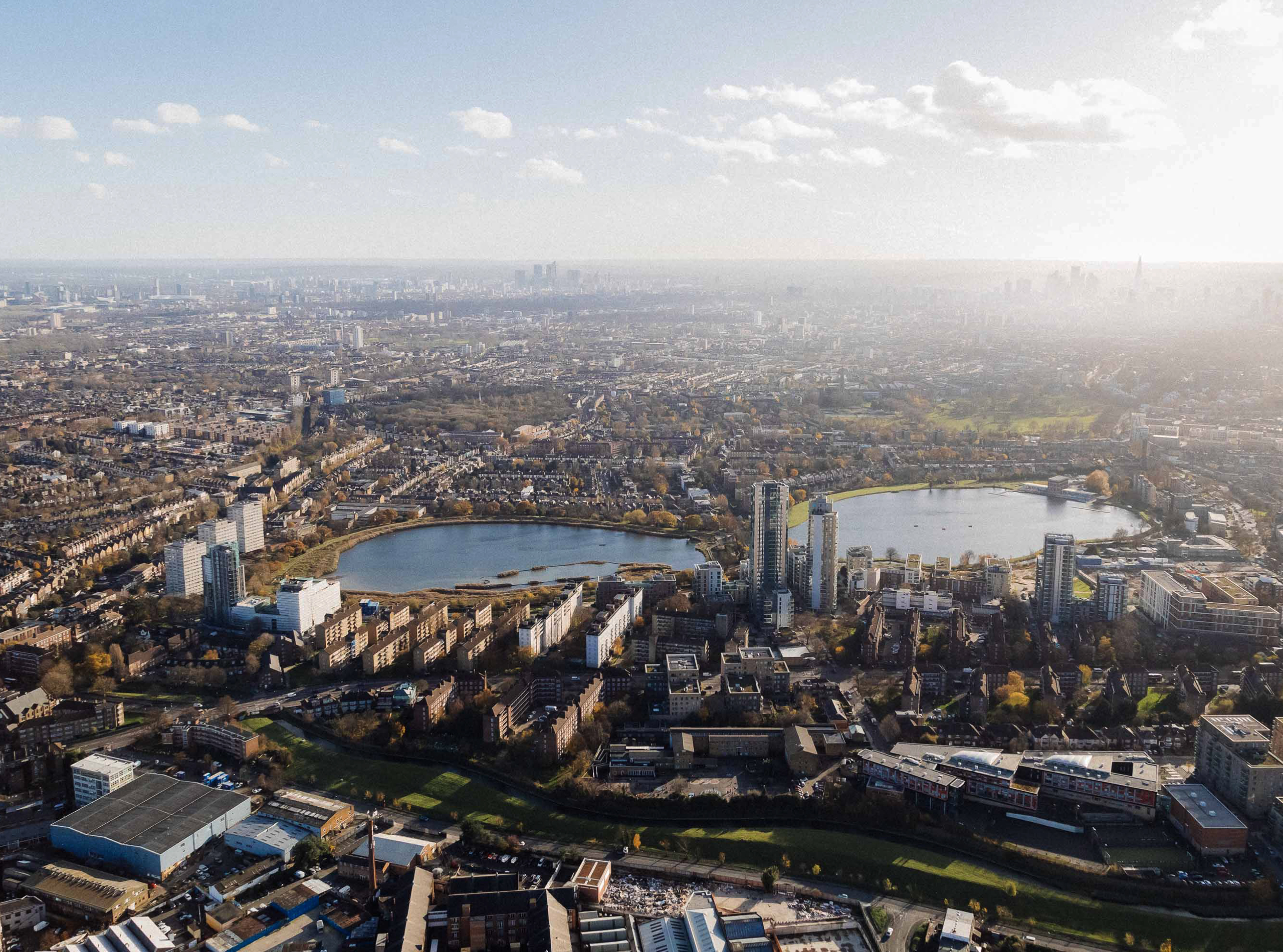
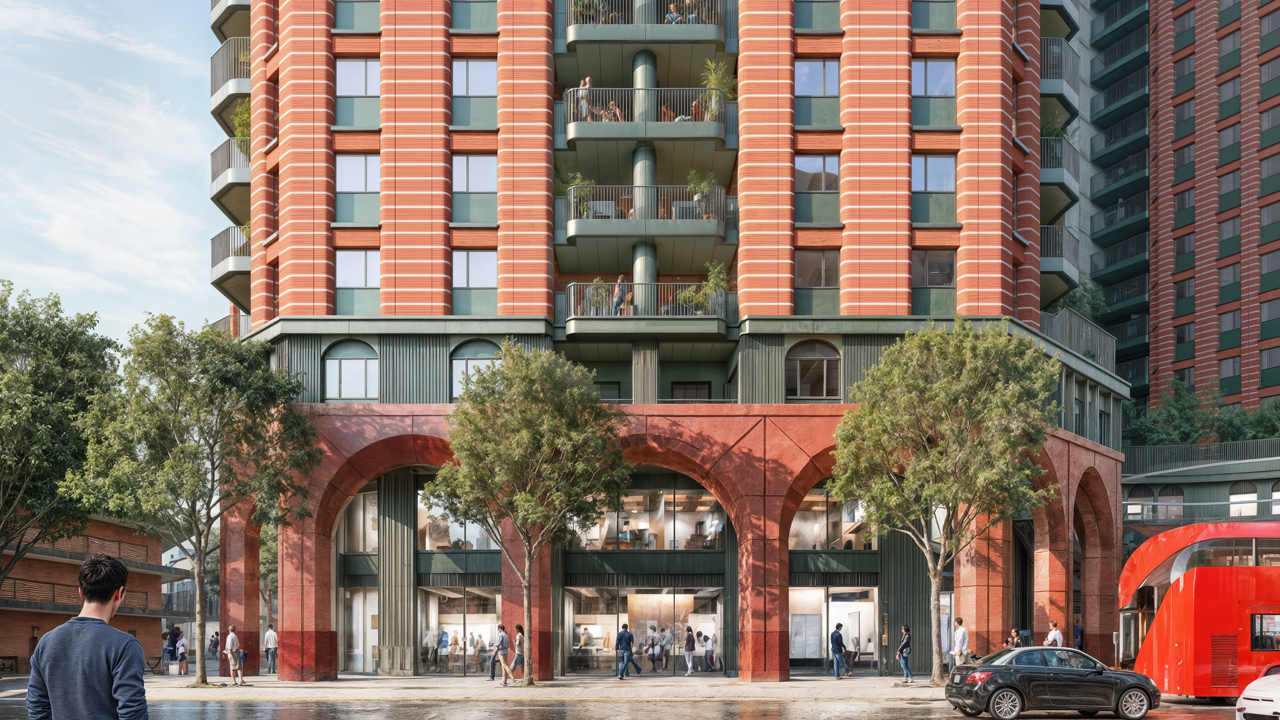
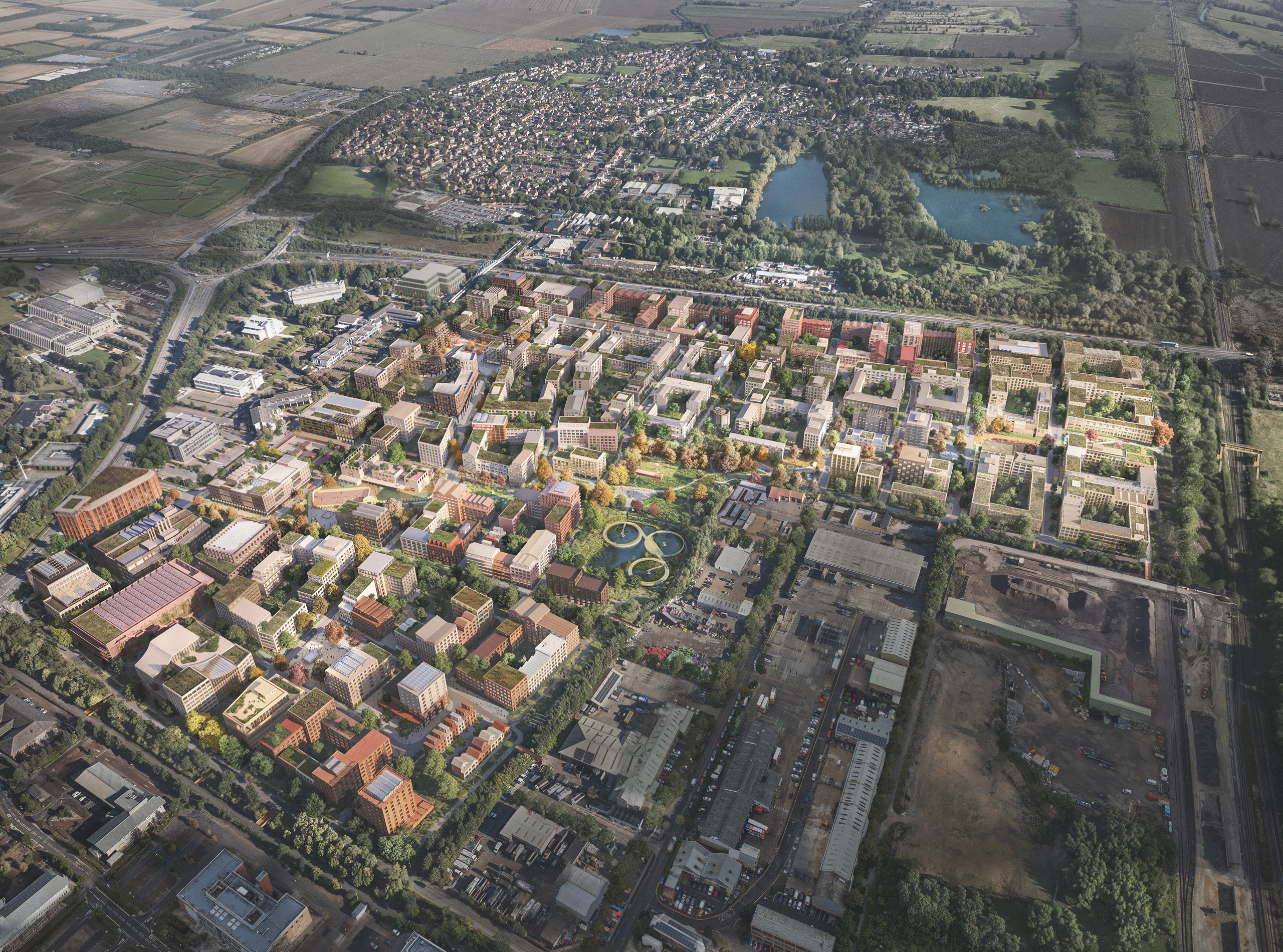
Covering 12,000 acres of parkland, farmland, and some of Europe’s most important ancient oak woodlands, The Blenheim Estate has a significant development portfolio encompassing residential, commercial, and agricultural properties across Oxfordshire.
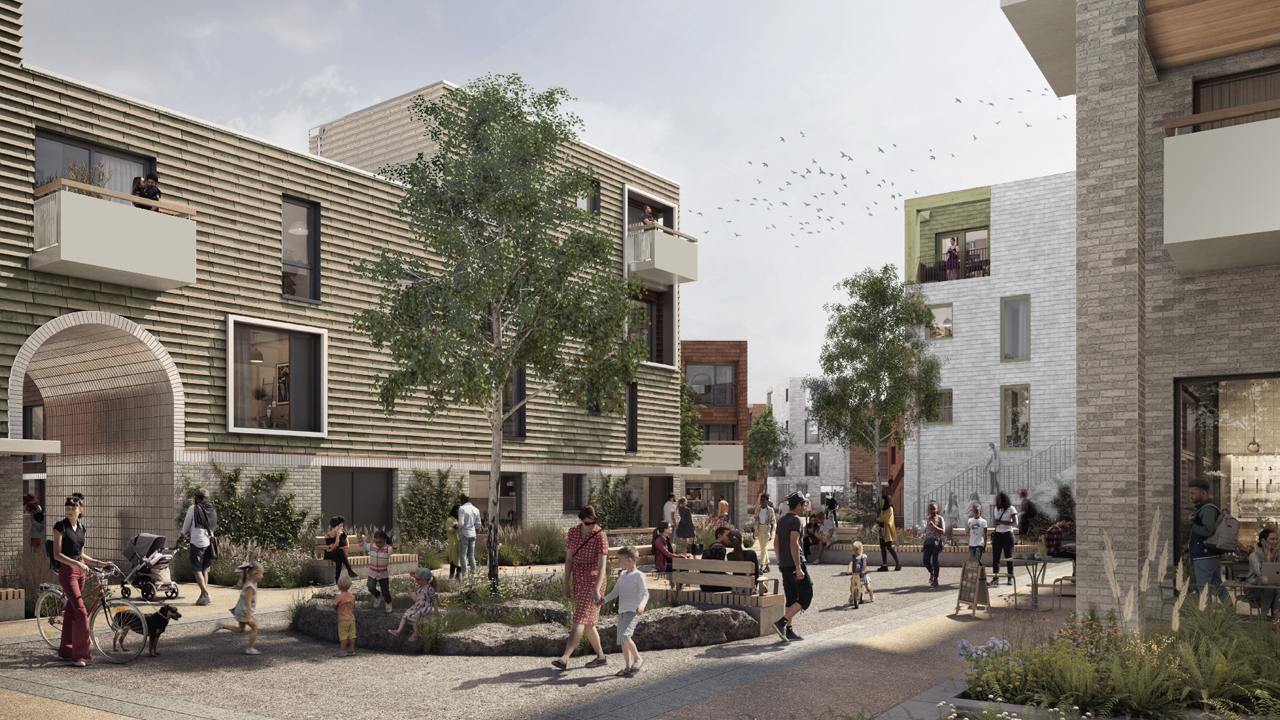
With unique opportunities to implement long-term sustainable development strategies, the project challenges traditional rural development approaches. Our infrastructure strategy addresses multiple technical challenges, including increasing resilience to climate impacts, enhancing natural habitats, and achieving energy self-sufficiency across the Estate’s communities.
These solutions operate within the constraints of an Area of Outstanding Natural Beauty (AONB), requiring innovative approaches that protect landscape character while enabling sustainable growth.
Environmental delivery
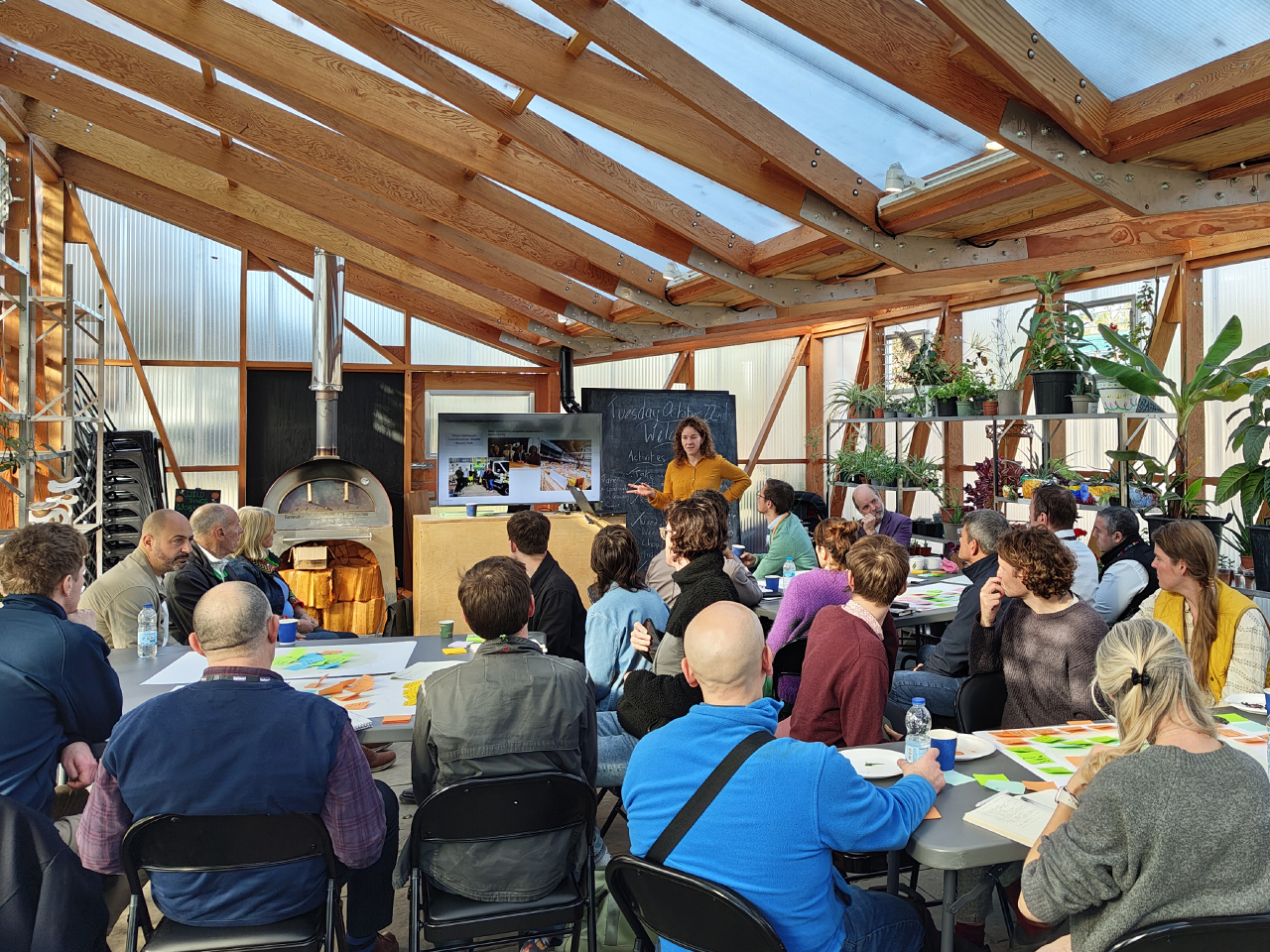
By utilising the VeloCity’s award-winning vision to inform our technical strategy, we drew from research that shaped the National Infrastructure Commission’s report, “Partnering for Prosperity: A new deal for the Cambridge-Milton Keynes-Oxford Arc”. This vision received international recognition, including honorary awards at the International Making Cities Livable Conference in Ottawa and the RIBA Research Fund, demonstrating innovative potential for rural transformation.
Our infrastructure strategy prioritises renewable energy systems that enable energy independence while maintaining landscape sensitivity. Technical solutions integrate distributed generation technologies with traditional rural infrastructure, creating resilient networks that reduce carbon emissions while supporting community growth through coordinated planning across neighbouring villages.
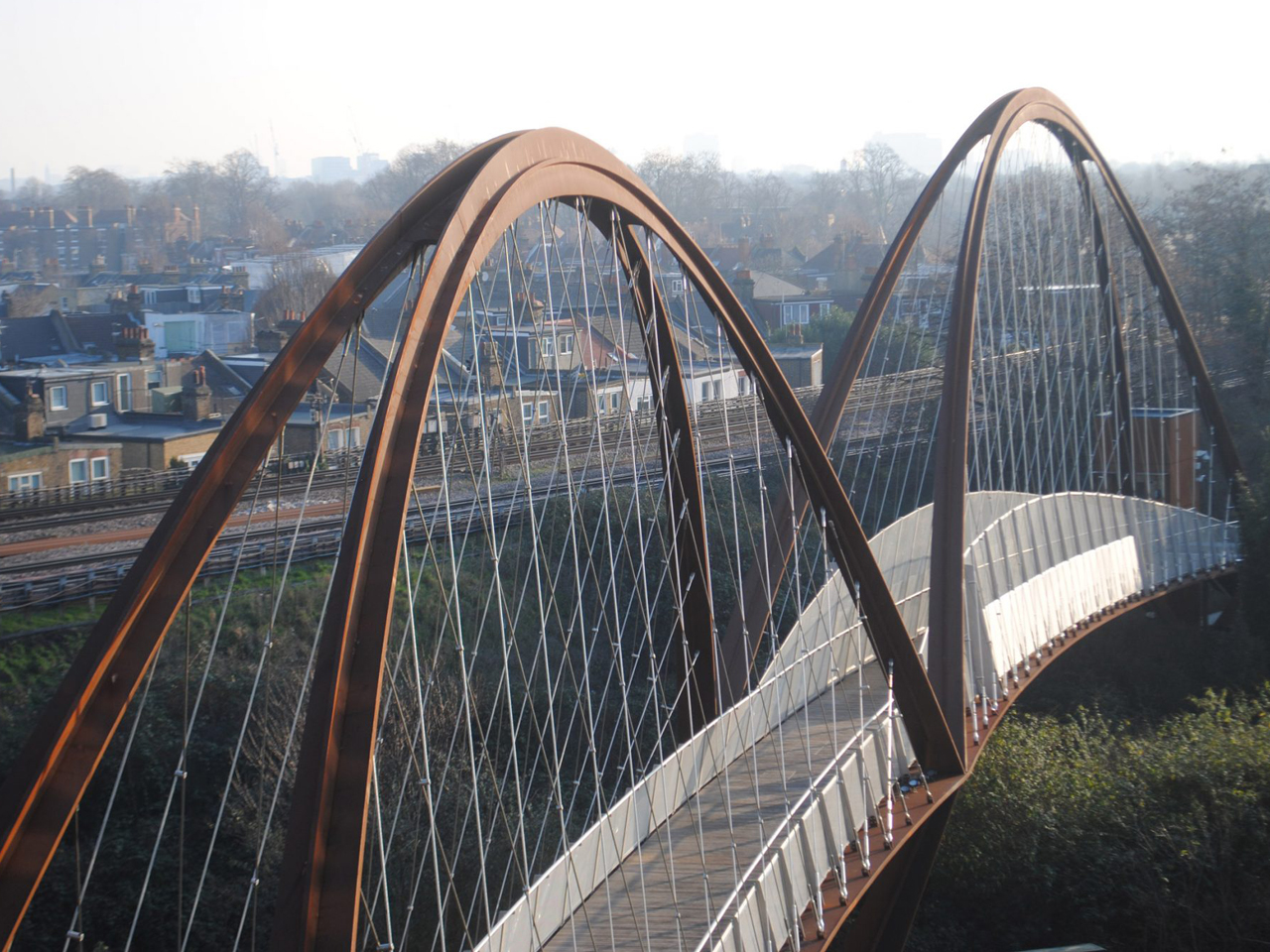
Climate resilience forms a central component of our technical approach, addressing flood risk, extreme weather events, and changing precipitation patterns. A focus on nature-based solutions enhances natural habitats while providing protective functions – integrating with the existing landscape features to create multi-functional infrastructure that supports both ecological and community needs.
Habitat enhancement strategies combine conservation objectives with infrastructure development, establishing biodiversity corridors that connect isolated habitats while supporting sustainable transport networks. Our approach demonstrates how technical infrastructure can actively contribute to environmental regeneration rather than simply minimising negative impacts.
Image gallery